How to manage stress effectively? Stress management tips.
Does an external event alone contribute to the whole stress? Or does it also depend on how we MANAGE stressful events?
“Am stressed because of my work”
“Am stressed because of my family”
There is an interplay of 3 factors (external events, our stress perception and our coping strategies to stressors) which determines how stressful or less stressful we feel in a situation. Usually we associate feeling stressful to the external situation we are facing, but we need to understand that there might be other factors which could worsen or improve stress
1)Stress Perception
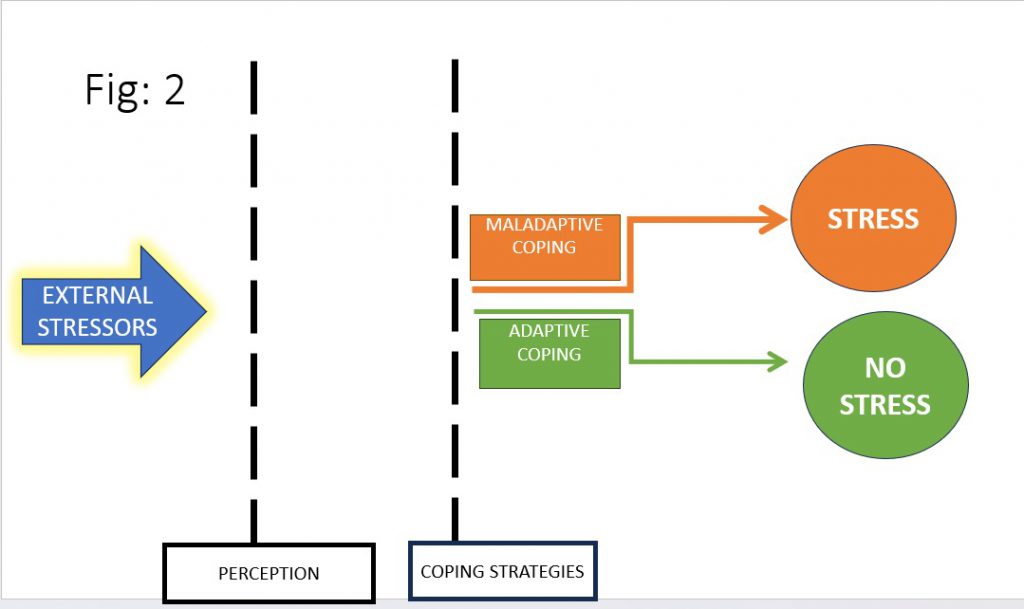
2)Coping strategies (FIG 2)
Stress perception: ‘Stressor’ refers to any situation/ event which is making us feel stressful So its important as how do we perceive or interpret our stressors? A situation may be perceived as “stressful” by one person and merely “challenging” by someone else.
1)Stress Perception
2)Coping strategies (FIG 2)
Stress perception: ‘Stressor’ refers to any situation/ event which is making us feel stressful So its important as how do we perceive or interpret our stressors? A situation may be perceived as “stressful” by one person and merely “challenging” by someone else.

EXAMPLE:
- A same event of a share market crash could be very stressful for some people and not so stressful for others who would understand its a part of Share market cycle!
- If a teacher is upset at their academic performance and shouting at all the students in the class, there could be a section of people who will take the criticism constructively and would improve their efforts and there could be another section who would start brooding about their inabilities and feel stressful.
So ‘stress perception’ is one major factor (not the only factor) in making someone stressful!
Lets do a task: List out major stressors with your life. Write out your ‘stress perception’ for those stressors as how are you perceiving those situations?
Coping strategies can be categorized into several types, and they can be adaptive or maladaptive
ADAPTIVE COPING
Adaptive coping strategies are those that help individuals effectively manage stress, overcome challenges, and maintain their emotional well-being.
These strategies promote long-term psychological health and resilience.
Example
- Problem-Solving: Adaptive coping involves identifying the source of stress and actively seeking solutions to address it. E.G: if someone is experiencing work-related stress, they may create a to-do list, delegate tasks, or seek advice from a colleague to manage their workload more effectively.
- Emotional Regulation: This involves recognizing and managing one’s emotional responses.
- Seeking Support: When individuals reach out to friends, family, or mental health professionals to discuss their concerns and gain emotional support, they are engaging in adaptive coping.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Engaging in activities such as regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep can be adaptive coping strategies that contribute to overall well-being.
Maladaptive Coping:
Maladaptive coping strategies are those measures that do not effectively address the stressors or challenges and may even exacerbate their distress. They may provide temporary relief but often lead to negative long-term consequences.
TAKE HOME MESSAGE…
Maladaptive coping strategies are those measures that do not effectively address the stressors or challenges and may even exacerbate their distress. They may provide temporary relief but often lead to negative long-term consequences.
- Avoidance: Avoidance involves ignoring or escaping from the source of stress rather than facing it.E.g a student who procrastinates on studying for an exam or someone who uses substances like alcohol or drugs to numb their emotions.
- Suppression: Suppressing emotions without venting and addressing it. For example, someone who pretends they are fine while struggling with grief may bottle up their emotions, which can have negative consequences in the long run.
- Self-Harm: Engaging in self-harming behaviors, such as cutting or burning, as a way to cope with emotional pain
- Denial: Denial involves refusing to acknowledge the existence of a problem or its impact.
- Escapism: Escapism involves using excessive screen time, excessive gaming, or other distractions as a way to avoid facing real-life problems. While these activities can offer temporary relief, they do not address the underlying issues.
TAKE HOME MESSAGE…
- More awareness about anxiety and depression is needed in prompt identification and early treatment.
- Its NOT RIGHT to ‘normalise’ Depression as mere sadness and Anxiety as fearfulness.
- High time to empathise with family/ friends/ colleagues about mental health problems.
- Got to understand it’s a problem in brain circuitry and neurotransmitters.
- Abstain from using terms like ‘mentally weak’, ‘weak person’ to people suffering from mental health problems.
